题目描述
leetcode 困难题
现有一棵无向、无根的树,树中有 n 个节点,按从 0 到 n - 1 编号。给你一个整数 n 和一个长度为 n - 1 的二维整数数组 edges ,其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示树中节点 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条边。
每个节点都关联一个价格。给你一个整数数组 price ,其中 price[i] 是第 i 个节点的价格。
给定路径的 价格总和 是该路径上所有节点的价格之和。
另给你一个二维整数数组 trips ,其中 trips[i] = [starti, endi] 表示您从节点 starti 开始第 i 次旅行,并通过任何你喜欢的路径前往节点 endi 。
在执行第一次旅行之前,你可以选择一些 非相邻节点 并将价格减半。
返回执行所有旅行的最小价格总和。
示例1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| 输入:n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3]], price = [2,2,10,6], trips = [[0,3],[2,1],[2,3]]
输出:23
解释:
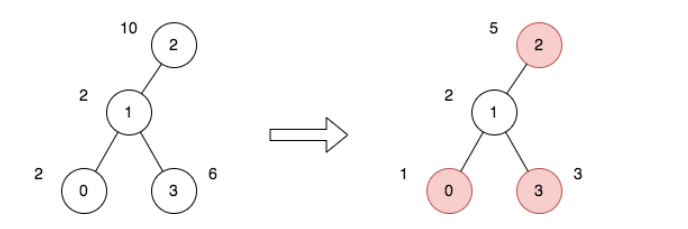
上图表示将节点 2 视为根之后的树结构。
第一个图表示初始树,第二个图表示选择节点 0 、2 和 3 并使其价格减半后的树。
第 1 次旅行,选择路径 [0,1,3] 。路径的价格总和为 1 + 2 + 3 = 6 。
第 2 次旅行,选择路径 [2,1] 。路径的价格总和为 2 + 5 = 7 。
第 3 次旅行,选择路径 [2,1,3] 。路径的价格总和为 5 + 2 + 3 = 10 。
所有旅行的价格总和为 6 + 7 + 10 = 23 。可以证明,23 是可以实现的最小答案。
|
提示1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| 1 <= n <= 50
edges.length == n - 1
0 <= ai, bi <= n - 1
edges 表示一棵有效的树
price.length == n
price[i] 是一个偶数
1 <= price[i] <= 1000
1 <= trips.length <= 100
0 <= starti, endi <= n - 1
|
树形 DP
需要注意的是贪心解法是错的,也就是说价格减半的点并不止两种情况,可以参考打家劫舍或者以下这个例子
最优的选择明显是将第一个和最后一个节点价格减半,而不是分奇偶节点。
没有陷入贪心解法的误区的话,其实问题就类似打家劫舍了。
不同的是我们需要求出每个节点的实际价格,而由于树上任意节点间的路径固定,所以我们只需要求出每个节点经过的次数,将该次数乘上原价格即可得出该节点的实际价格。
求每个节点的经过次数有两种做法:
暴力 DFS
注意到题目数据规模较小,可以暴力枚举所有旅行,将经过的点计数加一即可。
时间复杂度: $O(nq)$ ,$q$ 为旅行次数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| class Solution {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> g = new HashMap<>();
int[] cnt;
int[] price;
public int minimumTotalPrice(int n, int[][] edges, int[] price, int[][] trips) {
this.price = price;
cnt = new int[n];
for (int[] e : edges) {
g.computeIfAbsent(e[1], __ -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(e[0]);
g.computeIfAbsent(e[0], __ -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(e[1]);
}
Arrays.stream(trips).forEach(t -> tripCnt(t[0], t[1], -1));
return Arrays.stream(dfs(0, -1)).min().orElseThrow();
}
private boolean tripCnt(int node, int end, int fa) {
if (node == end) {
cnt[end]++;
return true;
}
for (int connect : g.getOrDefault(node, Collections.emptyList())) {
if (connect == fa) {
continue;
}
if (tripCnt(connect, end, node)) {
cnt[node]++;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private int[] dfs(int node, int fa) {
int val = cnt[node] * price[node];
int[] ret = new int[]{val, val / 2};
for (int connect : g.getOrDefault(node, Collections.emptyList())) {
if (connect == fa) {
continue;
}
int[] dp = dfs(connect, node);
ret[0] += Math.min(dp[0], dp[1]);
ret[1] += dp[0];
}
return ret;
}
}
|
Tarjan LCA + 树上差分
树上任意两个节点 $a、b$ 的路径等价于 $a -> lca(a, b) -> b$ ,维护 $cnt[i]$ 表示节点 $i$ 对其祖先节点的贡献,那么节点 $a$ 经过次数即为 $i$ 子树下所有 $cnt[i]$ 之和。
$cnt$ 的维护过程依赖差分,假设存在 $(a, b)$ 旅行,有:
- $cnt[a]$++
- $cnt[b]$++
- $cnt[lca]$–
- $cnt[fa[lca]]$–
总体更新完毕后,再自底向上更新差分值即可。
剩下问题为求旅行节点的 $lca$ ,可以通过 Tarjan 求出。
时间复杂度:$O(n + qlog(n))$ 。$n$ 和 $trip.length$ 出到 $1e5$ 时该解法同样适用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
| class Solution {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> g = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, List<int[]>> tripMap = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> lcaMap = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> faMap = new HashMap<>();
int[] uf;
int[] cnt;
int[] price;
public int minimumTotalPrice(int n, int[][] edges, int[] price, int[][] trips) {
this.price = price;
cnt = new int[n];
uf = IntStream.range(0, n).toArray();
for (int[] e : edges) {
g.computeIfAbsent(e[1], __ -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(e[0]);
g.computeIfAbsent(e[0], __ -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(e[1]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < trips.length; i++) {
tripMap.computeIfAbsent(trips[i][0], __ -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(new int[]{trips[i][1], i});
tripMap.computeIfAbsent(trips[i][1], __ -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(new int[]{trips[i][0], i});
}
tarjanLca(0, -1, new HashSet<>());
diffCnt(trips);
return Arrays.stream(dfs(0, -1)).min().orElseThrow();
}
private void tarjanLca(int node, int fa, Set<Integer> visit) {
faMap.put(node, fa);
visit.add(node);
for (int connect : g.getOrDefault(node, Collections.emptyList())) {
if (connect == fa) {
continue;
}
tarjanLca(connect, node, visit);
uf[connect] = node;
}
for (int[] q : tripMap.getOrDefault(node, Collections.emptyList())) {
if (!visit.contains(q[0])) {
continue;
}
lcaMap.put(q[1], find(q[0]));
}
}
private void diffCnt(int[][] trips) {
for (int i = 0; i < trips.length; i++) {
int[] t = trips[i];
cnt[t[0]]++;
cnt[t[1]]++;
int lca = lcaMap.get(i);
int lcaFa = faMap.getOrDefault(lca, -1);
if (lcaFa != -1) {
cnt[lcaFa]--;
}
cnt[lca]--;
}
}
private int[] dfs(int node, int fa) {
int[] ret = new int[]{0, 0};
for (int connect : g.getOrDefault(node, Collections.emptyList())) {
if (connect == fa) {
continue;
}
int[] dp = dfs(connect, node);
ret[0] += Math.min(dp[0], dp[1]);
ret[1] += dp[0];
cnt[node] += cnt[connect];
}
int val = price[node] * cnt[node];
ret[0] += val;
ret[1] += val / 2;
return ret;
}
private int find(int point) {
if (point != uf[point]) {
uf[point] = find(uf[point]);
}
return uf[point];
}
}
|
